MVC
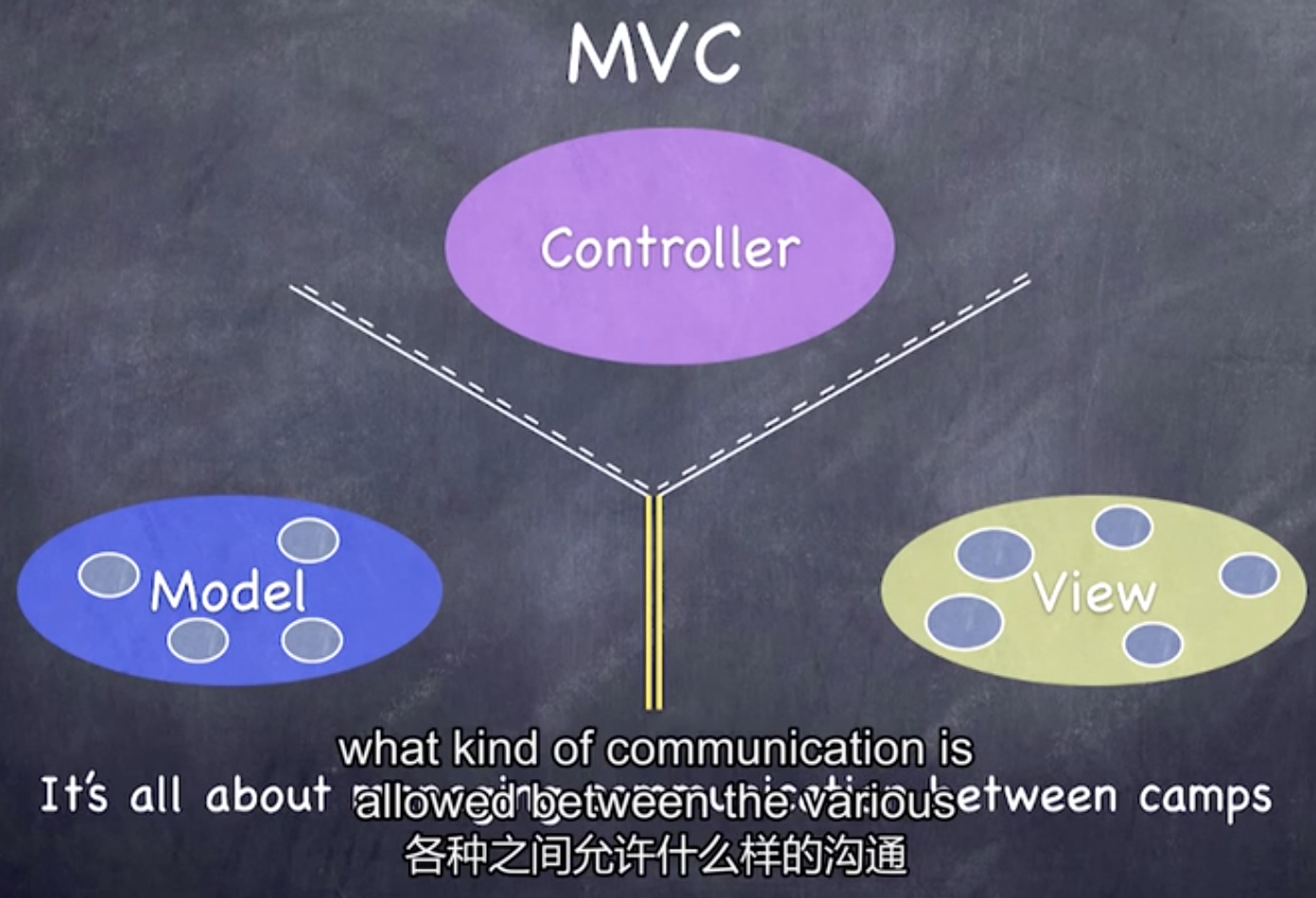
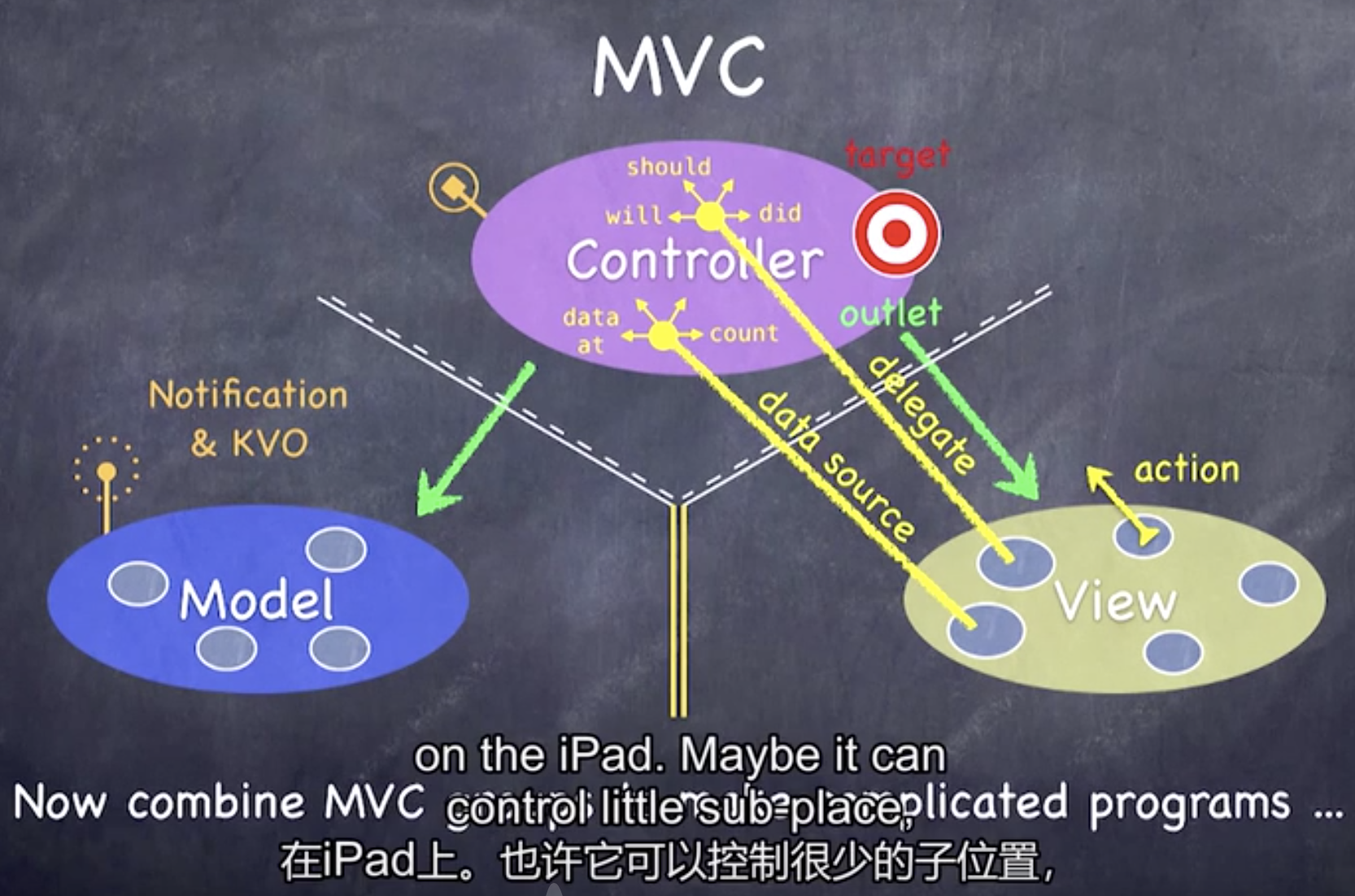
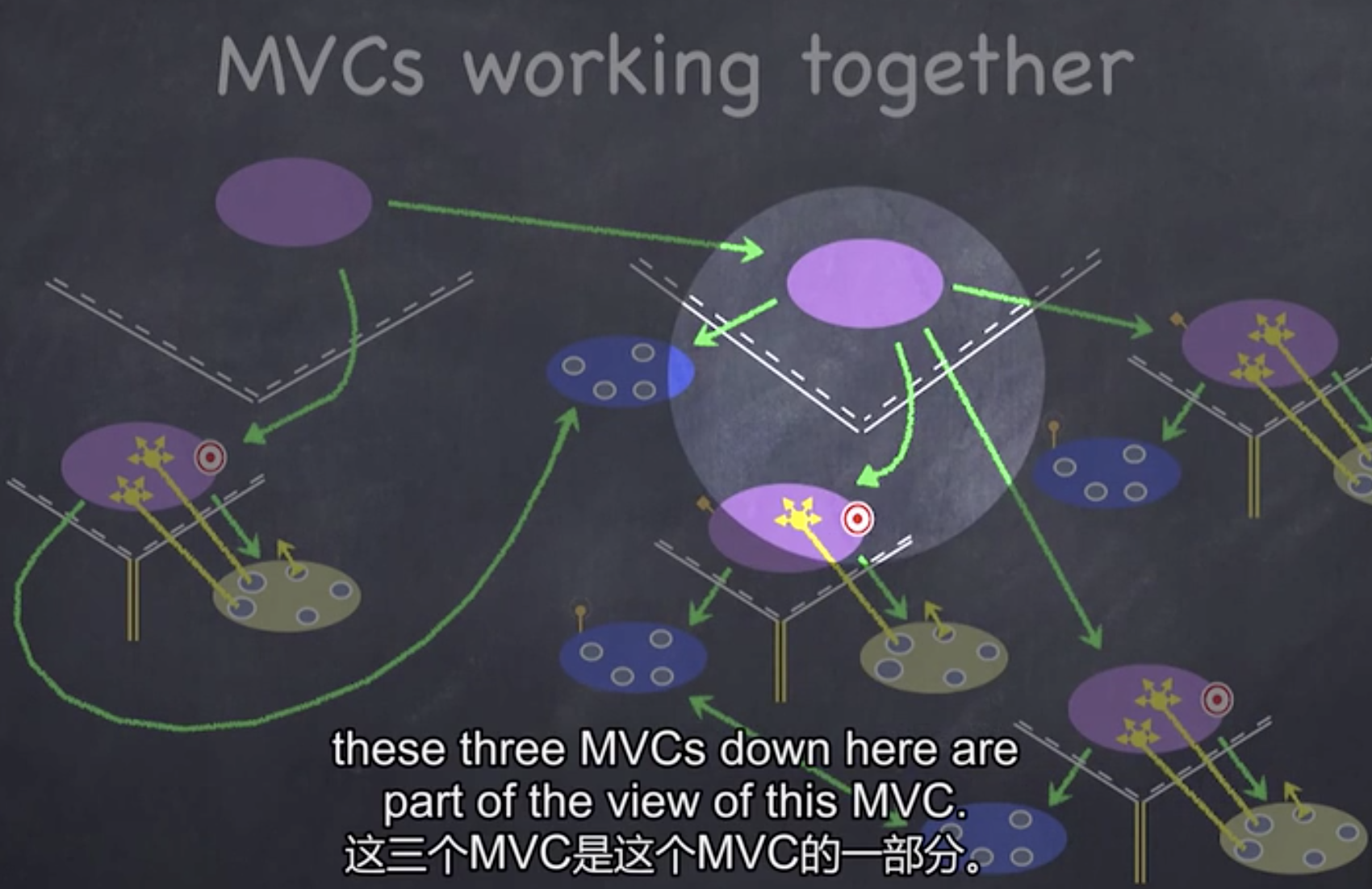
view: your controller’s minions (Main.storyboard)
controller: how your model is presented to the user — UI logic (ViewController.swift)
model: what your application is, but not how it is displayed (concentration.swift)
Model — Concentration.swift
API = Application Programming Interface: a list of all the methods and instancs variables in that class
public API: all the instanve variables and methods that you’re going to allow other classes to call
Initializer初始化
- 数组初始化
Array has an init with no arguments and what it does is it creates an empty array
var intArray = [Int]()
var yourArray = [String]()
var cards = Array<Card>()
var cards = [Card]()
- 类初始化
Concentration is a class, get a free init with no arguments as long as all of their vars are initialized.
var game: Concentration = Concentration()
- 结构体初始化
Struct, the free initializer they get, initializes all of their vars, even if they’re already pre-initialized.
类没有白送这种可以初始化所有变量的初始化器
let card = Card(isFaceUp: false, isMatched: false, indentifier: 1)
struct Card {
var identifier: Int
init(identifier: Int) {
identifier = identifier // 将传进来的identifier值赋值给Card的identifier
}
// 法一
// init tend to have the same internal name with alternal name
init(identifier i: Int) { // 外部参数名 内部参数名
identifier = i
}
// 法二
init(identifier: Int) {
self.identifier = identifier //通过self区分传入的identifier和Card的identifier
}
}
循环体
for … in … in后加sequence: array, string, countable range
// [0, numberOfPairsOfCards)
for indentifier in 0..<numberOfPairsOfCards {
}
// [1, numberOfPairsOfCards]
for indentifier in 1...numberOfPairsOfCards {
let card = Card(identifier: identifier)
// 法一
let matchingCard = card
cards.append(card)
cards.append(matchingCard)
// 法二
cards.append(card)
cards.append(card)
// putting things in an array or taking them out also copies the card
// 当翻转一张时,另一张不会翻转,因为是真实的副本,不是指针
// 法三
cards += [card, card]
}
// 用underbar作为control variable of loop,表示ignore this
for _ in 1...numberOfPairsOfCards {
let card = Card()
cards += [card, card] // 结构体是值类型,每次使用时复制
}
Stride is a global function that will create a CountableRange from floating point values. The return type of stride is CountableRange.
按照指定的递进值生成一个序列
through包含终点值ClosedCountableaRange
to不包含终点值CountableaRange
for i in stride(from: 0.5, through: 15.25, by: 0.3) {
}
遍历数组
for button in cardButtons {
}
// count数组长度
for index in 0...<cardButtons.count {
let button = cardButtons[index]
}
// indices = a countable range of all the indexes
for index in cardButtons.indices {
}
静态方法
Static function is a function even though it’s in the Card class, you can’t send it to a card
类内的静态方法不能传递给实例化对象,类似global function, utility function
struct Card {
// stored with each individual card -- card
var identifier: Int
// 静态变量stored with the type -- Card
static var identifierFactory = 0
// 静态方法
static func getUniqueIdentifier() -> Int {
// Card.identifierFactory += 1
// 静态方法内部can access静态变量,不需要Card.
identifierFactory += 1
return identifierFactory
}
}
延迟加载
Catch22: one depends on another
“catch-22 situation”意为本身就有问题、不符合逻辑而难以实现的规则或者进退两难的境地。
var game = Concentration(numberOfPairsOfCards: cardButtons.count / 2) // cardButtons还未初始化
property initializers run before ‘self’ is available
lazy var game = Concentration(numberOfPairsOfCards: cardButtons.count / 2)
If you make a var lazy, that means it doesn’t actually initialize until someone grabs it.使用时才初始化
所谓延迟加载就是在第一次访问某个属性时,要判断这个属性是否已经被初始化,如果已经初始化则直接返回,若没有初始化则进行初始化。这样可以把这个属性延迟初始化,把它和包含它的对象的初始化分隔开,来达到提升性能的目的。
链接:https://www.jianshu.com/p/d1c4cbb5bede
缺点:没有didSet
Random
伪随机数生成器
arc4random_uniform is a pseudo-random number generator, and it generates a random number between 0 and upper bound.
生成[0, 上限-1]之间的随机数,上限需为UInt32类型,count为Int类型,UInt32是struct,可用UInt32()初始化函数把Int转化为UInt32,同样Int()可将UInt32转化为Int类型
if emojiChoices.count > 0 {
let randomIndex = Int(arc4random_uniform(UInt32(emojiChoices.count)))
}